I challenged GROK to tell me whether NordaVinci’s Formula for the Area of a RIght Triangle is correct or not. At first it told me that it was wrong. Then I pushed the “think harder” button and it still said it was wrong. Then after thinking even harder with steam coming out of its ears. It finally admitted that it is correct.
Another day I asked it whether NordaVinci’s Formula can be used to prove the Pythagorean Theorem, which of course is simple to do. Again GROK stumbled and had to think harder and harder with steam coming out of its ears again. Finally it said “Yes” and compared it with ancient visual methods of doing that, which was interesting.
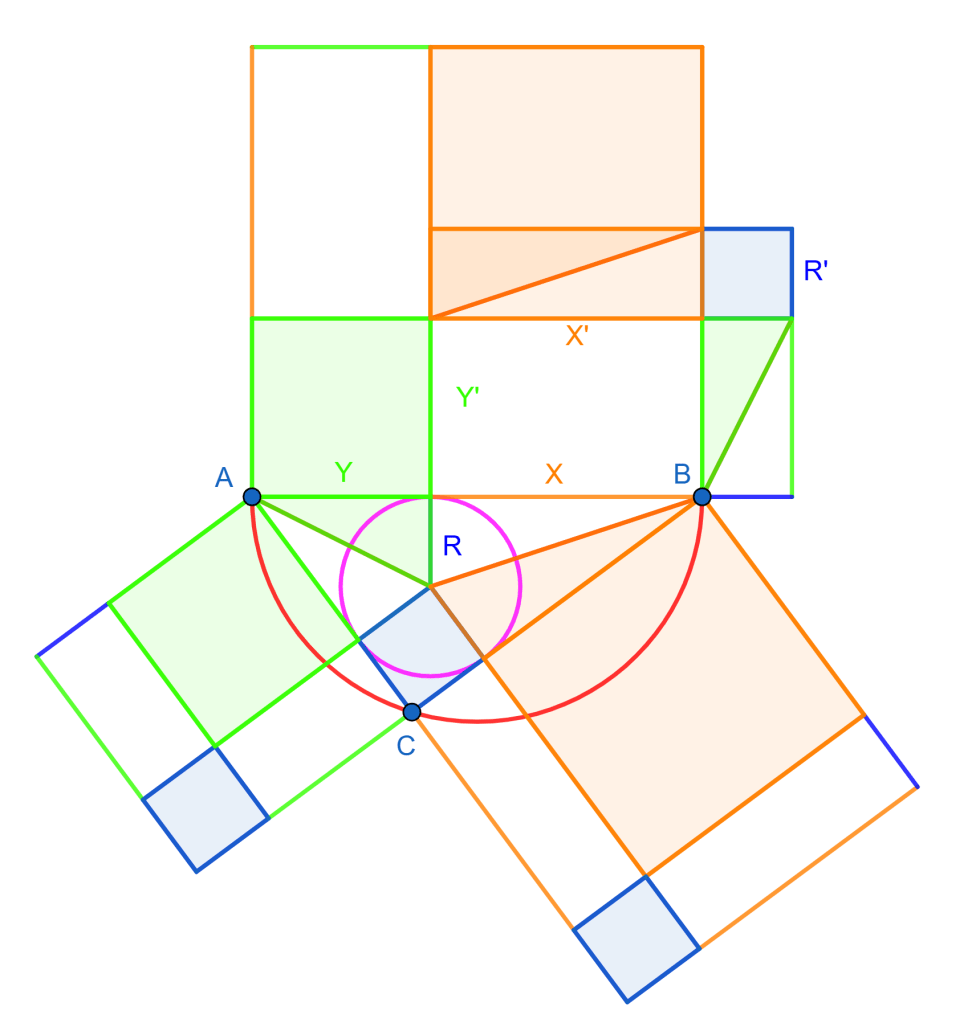
With that in mind, I produced a colorized diagram with GeoGebra (see GeoGebra.org) for anyone interested in having fun with GROK and geometry/trigonometry.
Diagram for visual proof of NordaVinci’s Formula for the Area of a Right Triangle –> X*Y = Area of Right Triangle ABC.
First prove that visually, and then using that, show visually that the Pythagorean Theorem is true.
The hypotenuse = X+Y. The adjacent sides are X+R and Y+R.
The Pythagorean Theorem states that (X+Y)^2 = (X+R)^2 + (Y+R)^2.
I just found out that . . .
Dr./Prof. Paul Yiu described this in his math problems p23 1998.
Euclidean Geometry
Preliminary Version
Paul Yiu
Department of Mathematics
Florida Atlantic University
Fall 1998
Z is a point on a segment AB such that AZ = u and ZB = v. Suppose
the incircle of a right triangle with AB as hypotenuse touches AB at
Z. Show that the area of the triangle is equal to uv. Make use of this
to give a euclidean construction of the triangle. 2
2Solution. Let r be the inradius. Since r = s − c for a right triangle, a = r + u and
LikeLike